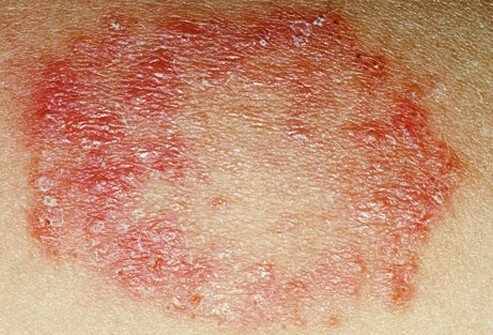
Bacterial skin infections are among the most common conditions encountered in both community and hospital settings. They can range from mild forms such as impetigo to severe, life-threatening infections like necrotizing fasciitis. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and preventive strategies are crucial in managing these infections effectively.
Understanding Bacterial Skin Infections
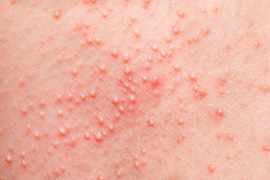
Bacterial skin infections occur when harmful bacteria invade the skin, leading to inflammation, redness, pain, and sometimes pus formation. The most common culprits include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Common Types of Bacterial Skin Infections:
Impetigo A highly contagious superficial infection, often affecting children.
Cellulitis A deeper infection involving the dermis and subcutaneous tissue.
Folliculitis Infection of the hair follicles.
Abscesses and boils Localized collections of pus that require drainage.
Erysipelas An infection causing raised, red, and painful patches of skin.
Each condition requires a tailored management strategy depending on severity, patient history, and underlying health issues.
General Principles of Management
Managing bacterial skin infections involves a combination of medical treatment, supportive care, and preventive measures.
1. Early Recognition
Prompt identification of symptoms such as redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, or drainage is essential. Delayed treatment can allow the infection to spread and complicate recovery.
2. Medical Treatment
Topical antibiotics (e.g., mupirocin) are effective for superficial infections like impetigo.
Oral antibiotics (e.g., cephalexin, clindamycin, doxycycline) are typically used for moderate infections.
Intravenous antibiotics are reserved for severe or systemic infections. Here, drugs like ceftriaxone play an important role, and reliable ceftriaxone injection distributors ensure hospitals and pharmacies maintain adequate supply.
3. Drainage Procedures
For abscesses or boils, surgical drainage is often necessary in addition to antibiotics.
4. Supportive Care
Rest, elevation of affected limbs, proper wound cleaning, and hydration aid recovery.
5. Preventing Recurrence
Good hygiene, treating underlying conditions (like diabetes), and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use can reduce recurrence.
Role of Antibiotics in Skin Infection Management
Antibiotics remain the cornerstone of treatment for bacterial skin infections. However, the choice of antibiotic depends on the type of infection, suspected pathogen, and resistance patterns.
Mild infections may respond to oral therapy.
Moderate-to-severe infections often require intravenous therapy.
Ceftriaxone, a third-generation cephalosporin, is highly valued for its broad-spectrum activity and once-daily dosing, making it suitable for outpatient and inpatient care. The availability of ceftriaxone often depends on trusted ceftriaxone injection distributors, who ensure that healthcare providers can deliver timely treatment.
Preventive Measures for Patients
Patients can take several steps to reduce their risk of developing or worsening bacterial skin infections:
Maintain proper hygiene Regular handwashing and daily showers help minimize bacterial load.
Treat minor cuts properly Cleaning small wounds promptly with antiseptic and keeping them covered.
Avoid sharing personal items Towels, razors, and clothing can spread bacteria.
Boost immunity A healthy diet, adequate sleep, and stress management strengthen the immune system.
Manage chronic conditions Diabetes, poor circulation, and immune disorders increase susceptibility to infections.
Hospital and Community Strategies
Beyond individual efforts, healthcare systems must also take proactive measures:
Surveillance programs to monitor antibiotic resistance patterns.
Education campaigns to encourage appropriate antibiotic use.
Reliable pharmaceutical supply chains to prevent shortages. The work of ceftriaxone injection distributors is crucial here, as delays in medication access can compromise patient outcomes.
The Importance of Timely Access to Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone remains a vital drug in the management of severe bacterial infections, including those affecting the skin. Its benefits include:
Broad-spectrum coverage against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Once-daily dosing, improving compliance.
Use in both hospital and outpatient settings.
However, global supply chain challenges and regional shortages can hinder availability. This is why the role of ceftriaxone injection distributors is not only logistical but also lifesaving. By ensuring hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies have uninterrupted access to this antibiotic, distributors help safeguard communities against serious infections.
Practical Tips for Patients and Caregivers
For those managing bacterial skin infections at home, these steps are recommended:
Follow the doctor’s prescription carefully Completing the full course of antibiotics prevents resistance.
Keep wounds clean and dry Use gentle antiseptic solutions and change dressings regularly.
Watch for warning signs Fever, spreading redness, or worsening pain may require urgent medical attention.
Avoid self-medication Misusing antibiotics can worsen resistance and delay proper care.
Antibiotic Resistance Concerns
One of the growing challenges in managing bacterial skin infections is antibiotic resistance. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to resistant strains such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
To combat this issue:
Physicians should prescribe antibiotics judiciously.
Patients should never pressure doctors for unnecessary antibiotics.
Hospitals and suppliers, including ceftriaxone injection distributors, must work together to ensure responsible distribution and usage of antibiotics.
Future Outlook
With the rise of resistant infections, researchers are exploring new antibiotics, vaccines, and alternative therapies such as bacteriophage treatment. Until then, prevention, timely diagnosis, and access to effective drugs like ceftriaxone remain the pillars of care.
Conclusion
Managing bacterial skin infections requires a multifaceted approach involving prevention, medical treatment, and responsible antibiotic use. Patients must practice good hygiene and adhere to prescribed therapies, while healthcare providers should stay updated on treatment guidelines and resistance trends. Importantly, access to effective antibiotics must be maintained through efficient pharmaceutical supply chains. Here, ceftriaxone injection distributors play a pivotal role, ensuring that hospitals and clinics have reliable access to one of the most important antibiotics in modern medicine.
By combining patient education, clinical best practices, and reliable access to essential drugs, communities can significantly reduce the burden of bacterial skin infections and improve overall health outcomes.








Write a comment ...